- Run Macos On Virtual Machines
- Run Mac On Virtual Machine In Windows
- Run Macos On Virtual Machine Free
- Run Macos On Linux Virtual Machine
- Run Linux On Mac Virtual Machine 2019
- Run Mac Os On Virtual Machine
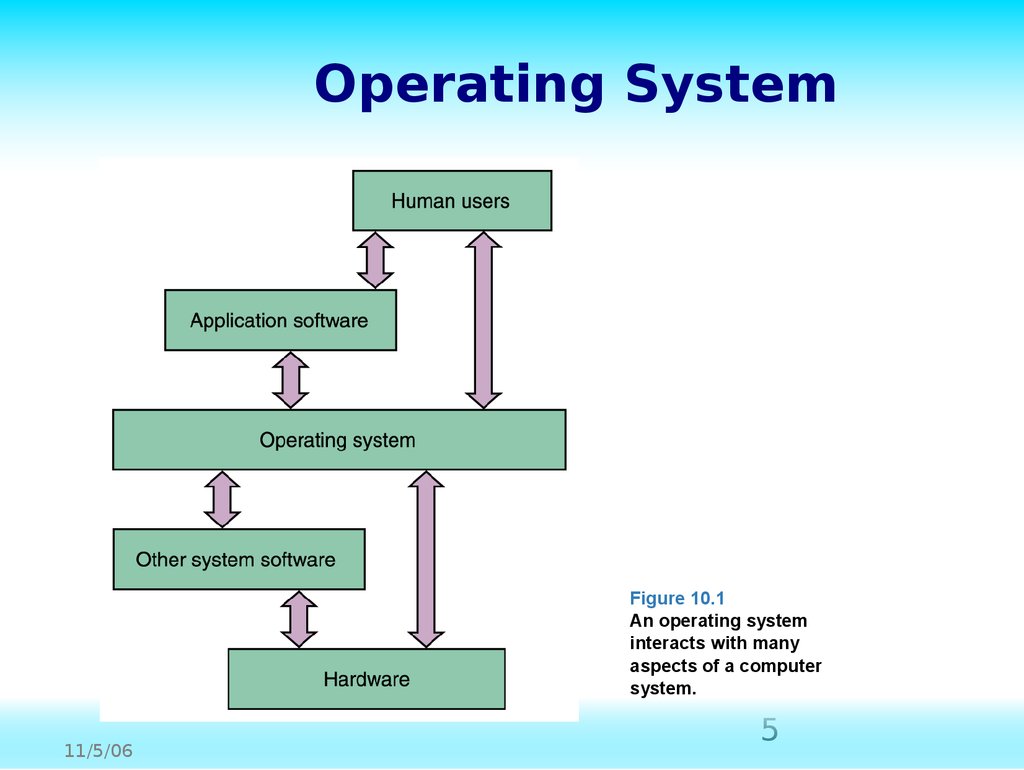
What is a virtual machine?
The virtual machine can then run alongside your normal Mac apps, such as Apple Mail and Safari, allowing you to run Windows and Mac apps on the Mac desktop at the same time. Whether you want to try out macOS, run Xcode or make a hackintosh you can use a virtual machine to get started on macOS. Remember the performance of macOS, particularly graphical support is very limited on a virtual machine so performance with graphical animations will be subpar compared to a real mac or hackintosh, but it will still get the job done. Yevgen is using the UTM app to run virtual machines on iOS devices, then has employed a process to create a virtual Hackintosh with a method shared on GitHub called OSX-KVM. KVM is an open source. Docker-OSX is a project that makes macOS run near native using OSX-KVM inside a Docker container. Using this, you'll be able to install macOS in a QEMU virtual machine (via Docker), and run the macOS Catalina or Big Sur desktop, or boot to the OSX shell. The Docker-OSX project provides four Docker images.
Sosumi is a snap package based on macOS-Simple-KVM that makes it easy to download and install macOS in a virtual machine (is comes bundled with qemu-virgil, which includes virtio-vga, a paravirtual 3D graphics driver).
A Virtual Machine(VM) is a compute resourcethat uses software instead of a physical computerto runprograms and deployapps. One or more virtual “guest” machinesrun on aphysical “host” machine.Each virtual machine runs its own operating systemand functions separately from the other VMs,even when they are all running on the same host. This means that, for example,a virtual MacOS virtual machine can run on a physical PC.
Get the latest edition of Next-Gen Virtualization for Dummies
Virtual machine technology is used for many use cases across on-premises and cloud environments. More recently, public cloud servicesare using virtual machines toprovide virtual application resourcesto multiple users at once, for even more cost efficient and flexible compute.
What are virtual machines used for?
Virtual machines(VMs) allow a business to run an operating system that behaves like a completely separate computer in an app window on a desktop. VMsmay be deployed to accommodate different levels of processing power needs, to run software that requires a different operating system, or to test applications in a safe, sandboxed environment.
Virtual machines have historically been used forserver virtualization, which enables IT teams to consolidate their computing resources and improve efficiency. Additionally, virtual machines can perform specific tasks consideredtoo risky to carry out in a host environment, such as accessing virus-infected data or testing operating systems. Since the virtual machine is separated from the rest of the system, the software inside the virtual machine cannot tamper with the host computer.
How do virtual machines work?
The virtual machine runs as a process in an application window, similar to any other application, on the operating system of the physical machine. Key files that make up a virtual machine include a log file, NVRAM setting file, virtual disk file and configuration file.
Advantages of virtual machines
Virtual machines are easy to manage and maintain, and they offer several advantages over physical machines:
VMs can run multiple operating system environments on a single physical computer, saving physical space, time and management costs.
Virtual machines support legacy applications, reducing the cost of migrating to a new operating system. For example, aLinux virtual machine running a distribution of Linux as the guest operating system can exist on a host server that is running a non-Linux operating system, such as Windows.
VMs can also provide integrateddisaster recoveryand application provisioning options.
Disadvantages of virtual machines
While virtual machines have several advantages over physical machines, there are also some potential disadvantages:
Running multiple virtual machines on one physical machine can result in unstable performance if infrastructure requirements are not met.
Virtual machines are less efficient and run slower than a full physical computer. Most enterprises use a combination of physical and virtual infrastructure to balance the corresponding advantages and disadvantages.
The two types of virtual machines
Users can choose from two different types of virtual machines—process VMs and system VMs:
A process virtual machineallows a single process to run as an application on a host machine, providing a platform-independent programming environment by masking the information of the underlying hardware or operating system. An example of a process VM is the Java Virtual Machine, which enables any operating system to run Java applications as if they were native to that system.
A system virtual machineis fully virtualized to substitute for a physical machine. A system platform supportsthe sharing of a host computer’s physical resources between multiple virtual machines, each running its own copy of the operating system. This virtualization process relies on ahypervisor, which can run on bare hardware, such as VMware ESXi,or on top of an operating system.
What are 5 types ofvirtualization?
All the components of a traditional data center or IT infrastructure can be virtualized today, with various specific types of virtualization:
Run Macos On Virtual Machines
Hardware virtualization:When virtualizing hardware, virtual versions of computers and operating systems (VMs) are created and consolidated into a single, primary, physical server. A hypervisor communicates directly with a physical server’s disk space and CPU to manage the VMs. Hardware virtualization, which is also known as server virtualization, allows hardware resources to be utilized more efficiently and for one machine to simultaneously run different operating systems.
Software virtualization:Software virtualization creates a computer system complete with hardware that allows one or more guest operating systems to run on a physical host machine. For example, Android OS can run on a host machine that is natively using a Microsoft Windows OS, utilizing the same hardware as the host machine does.Additionally, applications can be virtualized and delivered from a server to an end user’s device, such as a laptop or smartphone. This allowsemployees to accesscentrally hosted applications when working remotely.
Storage virtualization:Storage can be virtualized by consolidating multiple physical storage devices to appear as a single storage device. Benefits include increased performance and speed, load balancing and reduced costs. Storage virtualization also helps with disaster recovery planning, as virtual storage data can be duplicated and quickly transferred to another location, reducing downtime.
Network virtualization:Multiple sub-networks can be created on the same physical network by combiningequipment into a single, software-based virtual network resource. Network virtualization also divides available bandwidth into multiple, independent channels, each of which can be assigned to servers and devices in real time. Advantages include increased reliability, network speed,security and better monitoring of data usage. Network virtualization can be a good choice for companies with a high volume of users who need access at all times.
Desktop virtualization:This common type of virtualization separates the desktop environment from the physical device and stores a desktop on a remote server, allowing users to access their desktops from anywhere on any device. In addition to easy accessibility, benefits of virtual desktops includebetter data security, cost savingson software licenses and updates, andease of management.
Container vs virtual machine
Likevirtual machines, container technology such as Kubernetesissimilar in the sense of running isolated applications on a single platform. While virtual machines virtualize the hardwarelayer to create a “computer,”containers package up just a single app along with its dependencies.Virtual machines are often managed by a hypervisor, whereas container systems provide shared operating system services from the underlying host and isolate the applications using virtual-memory hardware.
A key benefit of containersis that they have less overhead compared to virtual machines. Containers include only the binaries, libraries and other required dependencies, and the application. Containers that are on the same host share the same operating systemkernel, making containers much smaller than virtual machines.As a result,containers boot faster, maximize server resources,and makedelivering applicationseasier. Containershave become popluar foruse cases such as web applications, DevOps testing, microservices and maximizing the number of apps that can be deployed per server.
Virtual machinesare larger and slower to boot than containers. They are logically isolated from one another, with their own operating system kernel, and offer the benefits of a completely separate operating system. Virtual machines are best for running multiple applications together, monolithic applications, isolation between apps, and for legacy apps running on older operating systems.Containers and virtual machines may also be used together.
Setting up a virtual machine
Virtual machines can be simple to set up, and there are many guides online that walk users through the process. VMware offers one such usefulvirtual machine set-up guide.
| Related Topics |
|---|
| Virtual Desktop Infrastructure Virtual Desktops Business Mobility Server Virtualization Network Virtualization Virtual Networking |

Run Mac On Virtual Machine In Windows
Run Macos On Virtual Machine Free
VMware Virtual Machine related Products, Solutions, and Resources
Hackintoshes – PCs tweaked to run macOS with workarounds have been around for a while. But as Apple only wants its software to run on its own devices, it’s become more difficult over time to actually use them as functional machines. Now a new type of Hackintosh appears to be gaining some traction that may be useful for research and educational purposes, virtual Hackintoshes. Interestingly, a video of an iPad running macOS has just surfaced as the latest virtual Hackintosh.
On YouTube, Yevgen Yakovliev shared an almost 40-minute walkthrough of what appears to be macOS Catalina running on a 2020 iPad Pro. Notably, this isn’t a method of running macOS Big Sur on the iPad Pro’s A12Z ARM chip.
Yevgen is using the UTM app to run virtual machines on iOS devices, then has employed a process to create a virtual Hackintosh with a method shared on GitHub called OSX-KVM. KVM is an open source Kernel-based Virtual Machine utility built into Linux.
Described by RedHat: “Specifically, KVM lets you turn Linux into a hypervisor that allows a host machine to run multiple, isolated virtual environments called guests or virtual machines (VMs).”
Notably, Kholia who posted the OSX-KVM resources on GitHub notes in the README that they are looking for help documenting the process of “running macOS on popular cloud providers (Hetzner, GCP, AWS).” It’s possible this example of macOS Catalina running on iPad could be a cloud-based Virtual Hackintosh.
As for the legality of all this, Kholia shared the following:
The “secret” Apple OSK string is widely available on the Internet. It is also included in a public court document available here. I am not a lawyer but it seems that Apple’s attempt(s) to get the OSK string treated as a trade secret did not work out. Due to these reasons, the OSK string is freely included in this repository.
Please review the ‘Legality of Hackintoshing’ documentation bits from Dortania’s OpenCore Install Guide.
Gabriel Somlo also has some thoughts on the legal aspects involved in running macOS under QEMU/KVM.
Run Macos On Linux Virtual Machine
You may also find this ‘Announcing Amazon EC2 Mac instances for macOS’ article interesting.

This is similar for macOS to what Apple took Correllium to court over with the latter offering iOS virtualization. Just last month, Corellium won part of the lawsuit.
Run Linux On Mac Virtual Machine 2019
Kholia also highlights:
My aim is to enable macOS based educational tasks, builds + testing, kernel debugging, reversing, and macOS security research in an easy, reproducible manner without getting ‘invested’ in Apple’s closed ecosystem (too heavily).
These Virtual Hackintosh systems are not intended to replace the genuine physical macOS systems.
Yergen also cited this post on virtualizing OpenCore and x86 as helpful in their work to get macOS working on the iPad Pro.
Run Mac Os On Virtual Machine
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links.More.
